What are terpenes?
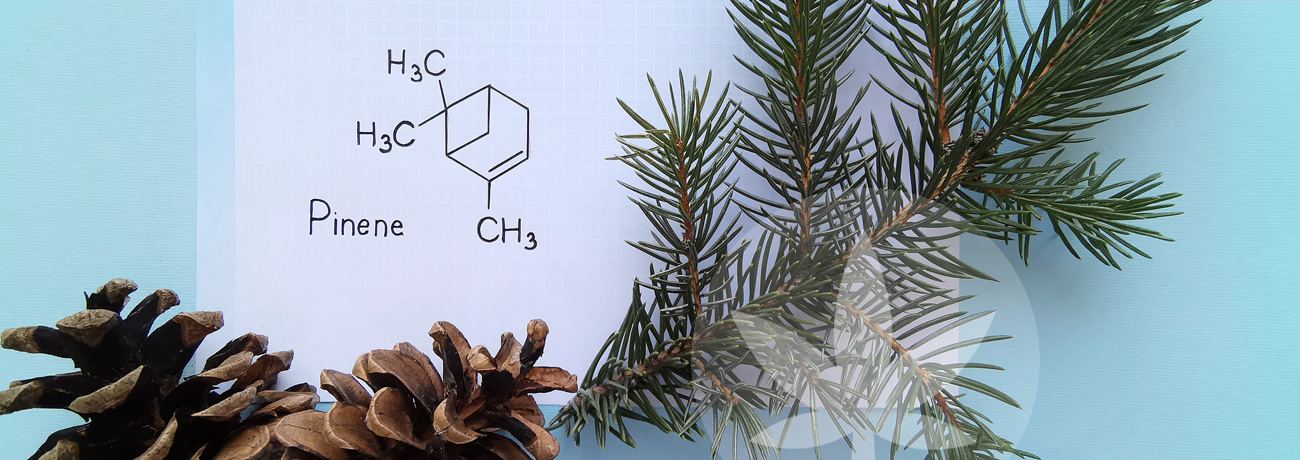
Terpenes may not be a familiar term, but in reality they're more common than you might think. But, what makes terpenes so important, and why does terpene content matter when it comes to full-spectrum CBD extracts? Keep reading to find out.
Contents:
What are terpenes and where do they come from?
First, let's start with what, exactly, a terpene is.
Terpenes are a large class of aromatic chemicals found in a wide variety of plants, foods, and essentials oils. Their primary purpose is to protect plants by repelling bacteria, fungi, and pests. But, as you'll discover, it's when we humans consume terpenes that they exhibit some really fascinating traits—traits you'll have likely experienced already. Why? Because terpenes are everywhere.
Black pepper, lavender, mint, mangoes, and lemongrass all contain terpenes! You'll even find terpenes in cleaning products, perfumes, and essential oils. Of course, we are mostly interested in the terpenes inside hemp, as the plant is an essential source of full-spectrum CBD extracts. It's believed over 200 different terpenes exist inside the plant, each with a slightly different chemical structure and, as a result, an exclusive aroma and a unique effect on the human body.
In hemp, you'll find terpenes in the trichomes; tiny, mushroom-shaped crystals that cover the leaves and flowers.
How many terpenes are there?
Although there are many different terpenes, some are more common than others. Well-known terpenes include:
• Myrcene
Myrcene is the most prominent terpene found in the Cannabis sativa species, but it also features heavily in clover, sage, hops, and caraway.
• Limonene
Remember the refreshing scent of lemon we mentioned earlier—that's because of limonene. This terpene is used heavily in perfumes, cosmetics, and air fresheners.
• Beta-Caryophyllene
Spicy and peppery, beta-caryophyllene is best known for its presence in black pepper, cloves, and cinnamon.
• Linalool
You'll instantly recognise the floral aroma of linalool. It's a pungent terpene most commonly found in lavender.

How terpenes are isolated from the hemp plant
Terpenes are extracted from hemp plant material in the same way as cannabinoids, via techniques such as supercritical CO₂ or alcohol extraction. But, terpenes are more sensitive to changes in temperature and pressure, so it's easy to damage them unless you have the equipment and expertise.
To understand how terpenes and cannabinoids exist together, imagine the hemp plant as a large glass jar.
First, we fill that jar with rocks; these are cannabinoids, the largest group of compounds. Next, we use smaller pebbles to fill in some of the gaps; these are our terpenes. Finally, to fill the jar, we pour in sand—flavonoids and other essential molecules.
You need all the elements outlined above to create a full-spectrum CBD extract, which is why sophisticated extraction is essential. In fact, supercritical CO₂ extraction is one of the few techniques that has the efficacy to isolate all of the essential compounds inside hemp (i.e. the rocks, pebbles, and sand), without damaging them.
How terpenes work
Researchers have identified dozens of ways that terpenes impact the human body, including influencing cell membranes, ion channels, receptors, and enzymes. But, when you consider how many terpenes there are, and how complex the human body is, it's no surprise they're still trying to figure out how each compound works.
Fortunately, a scoping review by the British Pharmacological Society[1] shed some light on the situation and found that terpenes exhibit "unique therapeutic effects that may contribute meaningfully to the entourage effects of cannabis‐based medicinal extracts". They even went on to add that interactions between cannabinoids and terpenes could lead to "synergy" concerning the treatment of dozens of biological conditions.
While we may not understand all of the interactions taking place, terpenes are proving to be quite versatile, potentially affecting:
• Mood
• Immune function
• Sleep
• Appetite
As the researchers highlighted, terpenes are significant not only because of their smell and possible biological effects, but because of their potential synergy with cannabinoids such as CBD, CBN, and CBG. There is evidence to suggest that when cannabinoids and terpenes exist together, their respective biological effects are enhanced.
This phenomenon—known as the entourage effect[2]—is what makes the molecules found within hemp unique. However, even in isolation, studies have shown that terpenes may have significant biological impacts of their own.
Can terpenes make you high?
Given how cannabinoids and terpenes synergise so well, and how terpenes can interact with various aspects of human physiology, it's common to wonder whether they will make you high. As far as researchers are aware, the terpenes found in hemp, and popular foods and essential oils, will not get you high.
To experience psychotropic side effects, a substance needs to interact with specific areas of our brain. Terpenes don't possess this ability, nor do they bind with CB receptors in the same way as psychotropic cannabinoids. Terpenes appear perfectly safe to consume, but it's worth highlighting that research on the matter is still limited.
Are terpenes legal?
Terpenes are considered legal all over the world, so you don't need to worry about the black pepper in your cupboards becoming an illicit substance. Even isolated terpenes are legal in the UK and US, but it's when you start to get your terpenes from the Cannabis sativa species that the situation becomes more complicated.
Fortunately, hemp is a widely accepted plant in most of the modern world. And, provided CBD products are manufactured to the correct standard, you'll have no issues with the cannabinoid or terpene content.
Why terpenes matter
From their synergy with cannabinoids to their dynamic influence on the body, terpenes are small aromatic compounds with a lot of potential.
That being said, there's still a lot to learn about how and why terpenes interact with specific biological processes or receptors. Thankfully, something researchers all agree on is the essential role terpenes play in full-spectrum CBD extracts, improving their efficacy compared to CBD isolates. With terpenes legal and safe to consume, it's never been easier to experience their boundless influence alongside the power of CBD.
If you want to experience the vast influence of terpenes, why not browse the Cibdol store for a complete range of full-spectrum CBD oils, capsules, and supplements? Or, if you’d like to learn more about how cannabinoids and terpenes work together, search our CBD Encyclopedia for everything you need to know.
[1] Russo, E. B. (2011). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology, 163(7), 1344–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01238.x [Source]
[2] Russo, E. B. (2018). The Case for the Entourage Effect and Conventional Breeding of Clinical Cannabis: No “Strain,” No Gain. NCBI. Published. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01969 [Source]
[1] Russo, E. B. (2011). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology, 163(7), 1344–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01238.x [Source]
[2] Russo, E. B. (2018). The Case for the Entourage Effect and Conventional Breeding of Clinical Cannabis: No “Strain,” No Gain. NCBI. Published. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01969 [Source]







