What's the Difference Between CBD and THC?
Published:
Cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are both compounds found in the cannabis plant. Though they share some similarities, there are key differences between these two cannabinoids.
Contents:
- CBD vs THC: The Highlighted Differences
- CBD Does Not Produce a High
- Is CBD Psychoactive?
- Legal Status of THC vs CBD
- Medicinal Uses: CBD vs THC
- Can CBD Counteract THC?
- CBD vs THC
- CBD and THC Similarities
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Does CBD show up on a drug test?
- Is CBD calming?
- Can CBD help me sleep?
- Will CBD get me high if I take a lot?
- Is THC better for pain relief?
- What's the best way to take CBD?
- What are the side effects of CBD?
- How does CBD work in the body?
- Is CBD beneficial for skin?
- What's better for anxiety: CBD or THC?
- How is CBD extracted from the cannabis plant?
- Is CBD legal internationally?
- What's the difference between full spectrum and broad spectrum CBD?
- What does CBD feel like?
- How is CBD different from hemp seed oil?
- How long does CBD stay in your system?
- Can you overdose on CBD?
- Does CBD build up in your system?
- Should CBD be taken with food?
- Is CBD safe for pets?
- What are terpenes?
- Summary

CBD vs THC: The Highlighted Differences
While CBD and THC have some overlapping qualities, there are distinct differences between the two:
- THC gets you high; CBD does not. THC is psychoactive, producing a “high” feeling. CBD lacks this mind-altering ability.
- CBD is non-intoxicating. It does not impair mental or physical functioning. THC can cause impairment.
- THC is illegal in most states. CBD extracted from hemp is legal in all 50 states.
- CBD has medicinal benefits. Both CBD and THC have therapeutic potential, but CBD has been more widely studied for its medicinal properties.
- CBD may counteract some THC effects. CBD may help balance some of the side effects of THC, like anxiety.
Let's explore these differences in more detail.
CBD Does Not Produce a High
The most notable difference between CBD and THC is their intoxicating effects.
THC is intoxicating. It binds directly to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and body, inducing euphoric and relaxing effects.
CBD lacks this binding affinity to cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it stimulates cannabinoid receptors indirectly, which modulates various receptor responses. This results in a calming effect without any high or impairment.
So in summary:
- THC causes intoxication and a high feeling
- CBD does not cause any high or impairment
This makes CBD appealing for those seeking therapeutic benefits without mind-altering effects.
Is CBD Psychoactive?
While CBD is non-intoxicating, does it have any psychoactive effects?
Psychoactive means affecting mental processes like mood, cognition, perception, and behavior. Unlike THC, CBD does not induce euphoria or cloud judgment. However, CBD does appear to produce subtle psychoactive effects.
CBD may alter perception of pain, anxiety, and sleep. Scientific studies show CBD may help relieve pain and inflammation, reduce anxiety, and improve sleep quality. These effects demonstrate CBD can mildly alter mood and perception.
So in summary:
- THC is intoxicating and psychoactive.
- CBD is not intoxicating but may be mildly psychoactive.
The subtle effects of CBD make it appealing for promoting mental wellness.

Legal Status of THC vs CBD
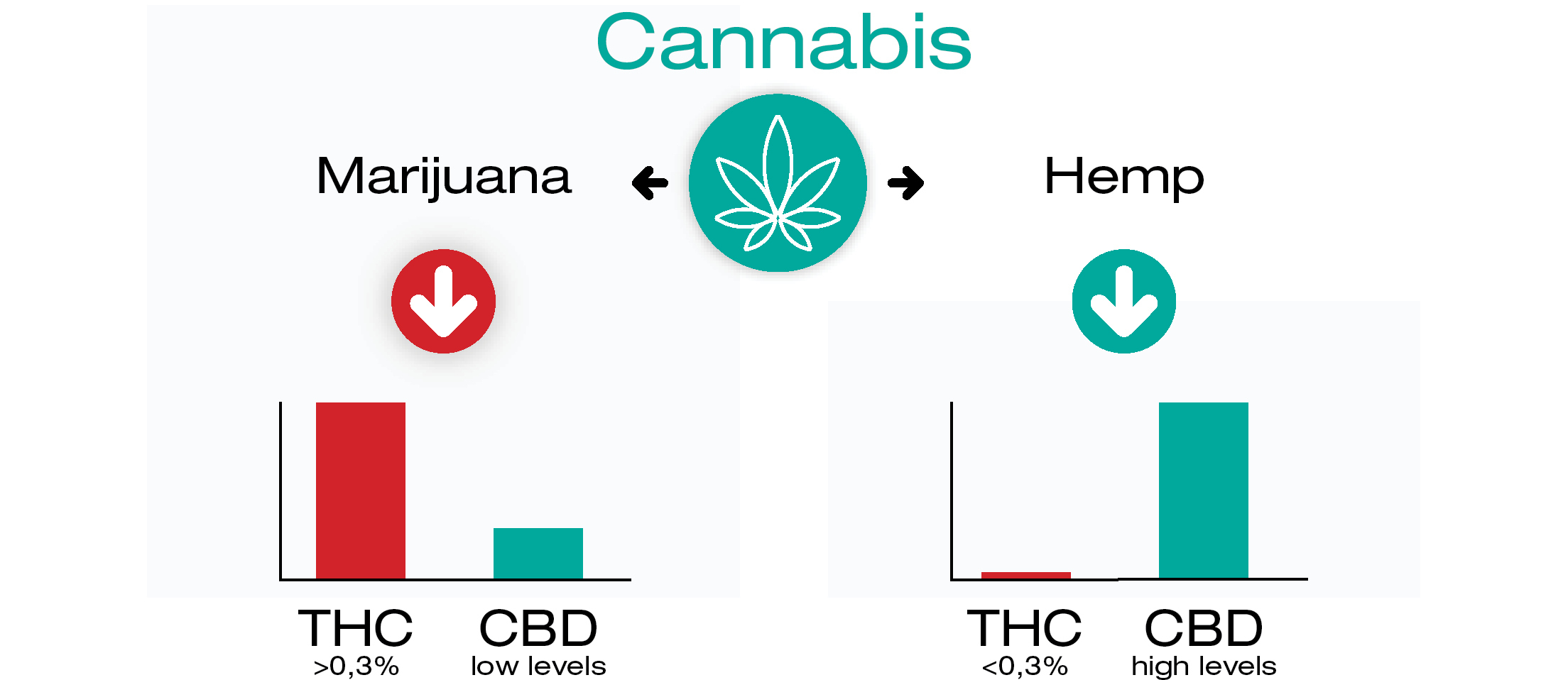
A key legal distinction between THC and CBD is whether the cannabis plant is marijuana or hemp.
Marijuana refers to cannabis plants with >0.3% THC content. Hemp refers to varieties with ≤0.3% THC.
THC from marijuana is illegal federally and in most states. However, many states have legalized marijuana for medical or recreational use.
CBD derived from hemp is legal in all 50 U.S. states. The 2018 Farm Bill federally legalized hemp and hemp-derived products, including CBD.
However, CBD products can contain up to 0.3% THC. At high doses, this THC content may cause a positive drug test or mild impairment.
So in summary:
- THC from marijuana is illegal federally and in most states
- Hemp-derived CBD is legal in all 50 states
The legal status makes hemp-derived CBD widely accessible for those seeking therapeutic benefits without psychoactivity.
Medicinal Uses: CBD vs THC
Both CBD and THC have therapeutic properties. However, CBD has been more extensively studied for its medical uses.
CBD appears highly effective for treating childhood epilepsy syndromes like Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. In fact, the FDA has approved a CBD oral solution called Epidiolex for treating these conditions.
There is also evidence that CBD may help with other health conditions:
- Chronic pain and inflammation
- Anxiety and depression
- Insomnia and other sleep disorders
- Nausea and vomiting
- Neurodegenerative diseases
- Skin conditions like acne, psoriasis, and eczema
Compared to CBD, there is less conclusive evidence on the medicinal benefits of THC. THC may help with:
- Nausea and vomiting, especially in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy
- Chronic pain and muscle spasms
- Insomnia
- Poor appetite and weight loss
Research is still emerging. But current evidence points to CBD having broader therapeutic applications compared to THC.
In summary:
- CBD has been more widely studied for medicinal uses
- The FDA has approved one CBD drug to treat childhood epilepsy
The expansive therapeutic potential makes CBD an exciting area of cannabis research.
Can CBD Counteract THC?
CBD and THC have contrasting effects on anxiety. While THC may exacerbate anxiety in some people, CBD can help relieve anxiety.
Several studies indicate that CBD may counterbalance the anxiety provoked by THC. By interacting with serotonin receptors, CBD appears to tone down the anxiety, paranoia, and psychotic symptoms sometimes caused by THC.
Through its indirect agonism of cannabinoid receptors, CBD seems to modulate the more intense psychoactive effects of THC. This suggests CBD might be useful for minimizing some THC side effects.
Some interesting research has looked into using a combination of THC and CBD for therapeutic purposes. A CBD-rich cannabis extract may enhance therapeutic benefit while reducing undesirable effects.
More research is still needed. But current evidence indicates CBD may help counteract some of the negative effects of THC, like anxiety, paranoia, and memory impairment.
In summary:
- THC can provoke anxiety and paranoia in some people
- CBD may help relieve THC-induced anxiety and psychotic symptoms
The balancing effects of CBD show its potential therapeutic role in regulating the effects of THC.
CBD vs THC
- CBD does not cause intoxication; THC causes a high feeling and intoxication.
- CBD is non-impairing; THC can cause impairment of mental and physical abilities.
- CBD products are legal in all U.S. states as long as they contain
- CBD has been more extensively studied for medicinal benefits, but both CBD and THC have therapeutic potential.
- CBD may help counteract some of the side effects of THC, like anxiety and psychosis.
In essence, CBD delivers therapeutic effects without any high. Its lack of impairment and legality make it widely accessible for health benefits.
CBD and THC Similarities
Although CBD and THC have key differences, they also share some similar attributes including:
- Being derived from the cannabis plant
- Interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system
- Having potential to treat medical conditions
- Possessing anti-inflammatory effects
- Relieving pain
- Stimulating appetite
- Anti-nausea effects
Both also have exceptional safety profiles and are well tolerated in most people.
So while CBD and THC have distinct differences that distinguish them, they also share some parallel properties and effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does CBD show up on a drug test?
Pure CBD will not cause a positive drug test. However, many CBD products contain trace amounts of THC that could trigger a positive result.
Avoiding full-spectrum hemp products containing even tiny amounts of THC reduces the risk of a failed drug test. Opt for broad spectrum or CBD isolate products to avoid any THC.
Is CBD calming?
Yes, CBD has shown calming effects in several clinical trials. Its relaxant properties arise from indirect stimulation of cannabinoid receptors. Many users report feelings of calm and peace after taking CBD. For many, CBD promotes a sense of relaxation without causing drowsiness.
Can CBD help me sleep?
Growing evidence supports the sleep-enhancing effects of CBD. Through its interactions with various neurotransmitter receptors, CBD may improve sleep quantity and quality. However, dosage is important. Lower doses of CBD tend to be more stimulating. Higher doses are more likely to have sedating effects that help sleep.
Will CBD get me high if I take a lot?
No, CBD will not cause intoxication in any dosage. Large doses may cause drowsiness, but CBD does not have psychoactive properties. It does not bind directly to cannabinoid receptors to generate a high like THC does. Rest assured CBD products will not get you high.
Is THC better for pain relief?
THC has shown strong pain relieving effects. However, CBD also reduces pain and inflammation effectively. In fact, CBD may amplify the therapeutic benefits of THC while decreasing side effects. Using a combination of CBD and THC for pain management could allow lower doses of THC to remain effective with fewer side effects.
What's the best way to take CBD?
Some of the most popular methods of taking CBD include tinctures, capsules, gummies, vaping, and topical products. The best delivery method depends on your preferences and needs. For example, gummies or capsules for convenient dosing, tinctures for fast absorption, vaping for quick effects, and topicals directly on the skin.
What are the side effects of CBD?
CBD is very well tolerated by most people with minimal side effects. Potential but uncommon side effects can include drowsiness, diarrhea, changes in appetite, and fatigue. CBD may also interact with certain medications. Talk to your doctor before using CBD if you take prescription medications.
How does CBD work in the body?
CBD interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, as well as other signaling systems. It binds indirectly to cannabinoid receptors and modulates their activity to exert effects. CBD also interacts with receptors for serotonin and GABA to influence anxiety, pain perception, and sleep.
Is CBD beneficial for skin?
Early research indicates CBD may help reduce symptoms associated with skin conditions. The anti-inflammatory properties may decrease redness and irritation. CBD also has antioxidant effects which may help combat signs of aging. Applying CBD topically may reduce localized pain, acne, and inflammation. However, more human studies are still needed.
What's better for anxiety: CBD or THC?
Research indicates CBD may be better for anxiety relief. CBD appears to reduce anxiety levels and improve mood. On the other hand, THC may increase anxiety, paranoia, and psychosis in some people. However, a CBD/THC combination could help optimize therapeutic effects while minimizing adverse reactions.
How is CBD extracted from the cannabis plant?
There are several techniques used to extract CBD from cannabis:
- CO2 extraction uses carbon dioxide under high pressure to pull out cannabinoids from the plant. It's the preferred method for producing high quality CBD.
- Ethanol extraction uses ethanol alcohol to strip CBD and other compounds from plant matter.
- Oil extraction infuses parts of the cannabis plant into a carrier oil like olive or coconut oil. The CBD can then be separated from the infused oil.
- Steam distillation uses hot steam to extract CBD-rich oil from the hemp plant. The steam forces the oil out of the plant.
Is CBD legal internationally?
The legality of CBD varies between countries. While CBD is widely available in places like the United Kingdom and Canada, it remains illegal in other parts of the world. Some countries only permit CBD if it contains no THC. Local laws should always be consulted before purchasing CBD products internationally.
What's the difference between full spectrum and broad spectrum CBD?
Full spectrum CBD retains all the plant compounds found in cannabis, including THC. Broad spectrum CBD goes through added processing to remove THC but maintains other cannabinoids and terpenes. Broad spectrum CBD allows you to reap the "entourage effect" while avoiding THC.
What does CBD feel like?
CBD affects everyone differently. Most report a subtle sense of relaxation and calm after taking CBD. However, CBD will not cause mental impairment or intoxication. Larger doses are more likely to produce drowsiness. Topical CBD products provide targeted effects where applied but no full-body feeling.
How is CBD different from hemp seed oil?
Hemp seed oil comes from only the seeds of Cannabis sativa and contains no CBD. CBD oil is extracted from the flowers and leaves. Hemp seed oil has nutritional value but does not provide medicinal benefits. CBD oil has no nutritional value but may improve health issues like pain and anxiety.
How long does CBD stay in your system?
CBD is metabolized rather quickly in the body and is eliminated in a few days. However, the exact time CBD stays in your system depends on dosage, frequency of use, and mode of administration. Ingested CBD typically remains for 1-2 days while inhaled CBD stays for up to 3 days. CBD accumulates with chronic use.
Can you overdose on CBD?
It is impossible to fatally overdose on CBD. Even extremely high doses of CBD are well tolerated in humans and animals without dangerous side effects. However, very large amounts of CBD may cause drowsiness, diarrhea, dry mouth, and changes in appetite. Most symptoms resolve within a few days of stopping CBD.
Does CBD build up in your system?
Yes, CBD can accumulate in the body over time with repeated use. CBD has a 4-5 day half-life so levels steadily increase with daily administration. Full equilibrium in the bloodstream may take 2-4 weeks. At equilibrium, the amount of CBD getting metabolized equals the amount being administered.
Should CBD be taken with food?
Taking CBD with food enhances absorption, especially high-fat foods. Fatty acids boost bioavailability allowing more CBD to enter circulation. However, absorption is slower compared to taking CBD sublingually. Ultimately it depends if you prioritize faster effects or maximum absorption. Taking CBD on an empty stomach works too.

Is CBD safe for pets?
Anecdotal reports and veterinary research suggest CBD is generally safe for pets. However, the optimum dosages for animals are much lower than human doses. Potential side effects include lethargy and gastrointestinal upset. Always consult a veterinarian before giving CBD to pets.
What are terpenes?
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in many plants including cannabis. They give each cannabis strain its unique scent and flavor. Terpenes also interact synergistically with cannabinoids like CBD through the “entourage effect” to enhance therapeutic effects. Common cannabis terpenes include limonene, myrcene, and linalool.
Summary
CBD and THC are both compounds found in the cannabis plant. While they share some similarities, there are important distinctions between these two cannabinoids.
Most notably, THC is intoxicating while CBD is not. THC induces euphoric and psychoactive effects by directly binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain. This gives THC properties that can impair mental and physical functioning. In contrast, CBD does not directly stimulate cannabinoid receptors and simply does not get you high, no matter the dosage.
However, CBD is not completely devoid of psychoactive effects. It can subtly influence mood, pain perception, anxiety, and sleep through indirect interactions with the endocannabinoid system. But these effects are mild and CBD remains non-impairing.
Unlike THC, CBD derived from hemp containing less than 0.3% THC is legal at the federal level and in all 50 US states. The legal status and accessibility of CBD makes it appealing for those seeking therapeutic benefits without the high, impairment, or legal risk associated with THC.
Both CBD and THC have therapeutic potential and can help with conditions like chronic pain, nausea, insomnia, and appetite loss. However, CBD has been more extensively studied for medical applications and shows promise for childhood epilepsy, anxiety, depression, inflammation, neurodegenerative disease, and more. In fact, the FDA has approved one CBD-based drug for treating childhood seizure disorders.
Interestingly, CBD may help counterbalance some of the undesirable effects of THC such as anxiety, paranoia, and impaired memory. By interacting with serotonin and GABA receptors, CBD can potentially relieve anxiety provoked by THC. More research is still needed, but this demonstrates the therapeutic potential of CBD in regulating THC effects.
In summary, key differences between the two cannabinoids include:
- THC causes intoxication, CBD does not
- CBD is non-impairing, THC can impair mental and physical functioning
- CBD is legal federally, THC remains federally illegal
- CBD has been more widely researched for medical uses
- CBD may help minimize side effects of THC
CBD offers a clear-headed, non-impairing option to experience potential health and wellness benefits without the high of THC. With its safety profile and broad therapeutic promise, CBD is an exciting prospect for many seeking supplemental or alternative treatment options.















