Collagen: Boosting Health, Skin, and Joint Mobility
Published:
As a fundamental part of our anatomy, collagen is essential for sustaining health and well-being. This complex molecule is responsible for providing structural support to various connective tissues such as skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels and even tooth cells. In this comprehensive guide on collagen, we will explore its different types and benefits.
Contents:
- What is Collagen?
- Definition of Collagen
- Types of Collagen
- Benefits of Collagen
- Sources of Collagen
- How Does the Body Use Collagen?
- How Much Collagen Should I Take?
- How Long Does it Take for Collagen Supplements to Work?
- How to Restore Collagen in the Face
- Potential Side Effects of Taking Too Much Collagen
- Frequently Asked Questions Collagen
- Conclusion
We will delve into natural sources of collagen along with supplements that can help increase your intake. Additionally, we'll discuss how our bodies utilize collagen to maintain skin health and appearance while promoting joint mobility and bone strength.
As you continue reading this blog post about collagen peptides and their effects on dermal fillers or osteogenesis imperfecta treatment options among others; learn about recommended daily intake guidelines based on individual needs. Discover how long it takes for these supplements to work effectively against common concerns like joint pain or skin aging.
Finally, uncover various methods to restore facial collagen through dietary changes alongside topical treatments or professional procedures while being aware of potential side effects associated with excessive consumption of these products.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is a vital protein that makes up a significant portion of our body's structure, providing strength and elasticity to various tissues such as skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It plays an essential role in maintaining the integrity of these structures and ensuring their proper functioning. In this section, we will explore the definition of collagen, its different types, and its numerous benefits.
Definition of Collagen
Collagen is derived from the Greek word "kolla," meaning glue; it acts as a binding agent within our bodies' connective tissues. It forms long chains called fibrils that create a strong network for cells to attach to one another. This structural support allows our skin to maintain its firmness while also giving flexibility to joints and muscles.
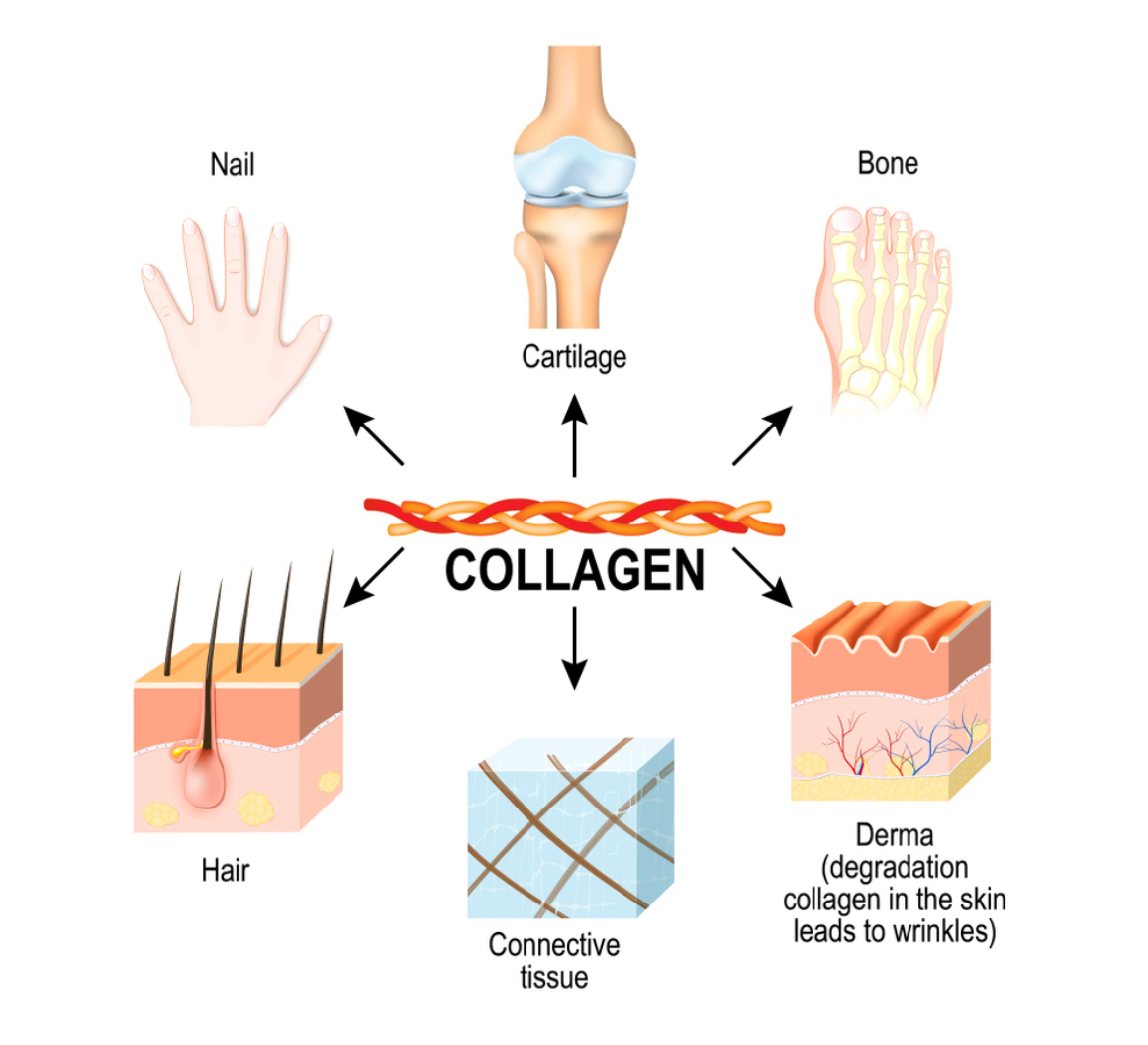
Types of Collagen
There are at least 28 known types of collagen,, but three main types make up about 80-90% of all collagens found in the human body:
- Type I: The most abundant type present in skin, tendons, organs & bone tissue - responsible for providing tensile strength & resistance against stretching.
- Type II: Found primarily in cartilage - contributes significantly towards cushioning joints & maintaining joint health.
- Type III: Present alongside Type I collagen in skin & blood vessels - helps provide elasticity & suppleness.
Benefits of Collagen
Collagen has many advantages that can help improve overall health and well-being. Some of the most notable advantages include:
- Skin Health: As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. Supplementing with collagen can help improve skin elasticity and hydration.
- Joint Health: Collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining joint function by providing cushioning between bones & reducing friction during movement. Taking collagen supplements may possibly aid in relieving joint soreness that is caused by osteoarthritis or other progressive conditions.
- Bone Density: Collagen is an essential component of bone structure, contributing to its strength & flexibility. Studies have shown that collagen supplementation can positively impact bone mineral density in postmenopausal women at risk for osteoporosis.
In addition to these primary benefits, research suggests that collagen may also aid in muscle mass maintenance, wound healing, gut health improvement, and hair/nail growth support.
Collagen is an important protein found in the body and it has a variety of benefits. To ensure adequate collagen intake, it is beneficial to look at sources of natural collagen as well as supplements and foods high in this nutrient.
Sources of Collagen
To ensure we have enough collagen, it's crucial to consume foods rich in this protein or consider taking supplements if necessary. In this section, we will explore natural sources of collagen, supplements for increasing collagen intake, and foods high in collagen.
Natural Sources of Collagen
The primary natural source of collagen is animal-derived products such as bone broth, chicken skin, fish with skin on (like salmon), and gelatin from grass-fed cows. Consuming these foods can help increase your body's production of collagen, leading to healthier skin, joints, bones and more.
Supplements for Increasing Collagen Intake
If you're unable to get enough collagen through diet alone or prefer a more convenient option for boosting your intake levels; there are several types of collagen supplements available on the market:
- Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides: These are easily digestible forms derived from bovine or marine sources that can be mixed into beverages like coffee or smoothies.
- Gelatin Powder: Derived from animal bones and connective tissue; it can be used as a thickening agent when making soups or stews.
- Capsules/Tablets: Containing either hydrolyzed peptides or other bioactive compounds designed to support healthy collagen production.
Foods High in Collagen
In addition to the natural sources mentioned earlier, there are several other foods high in collagen that you can incorporate into your diet:
- Eggs: The whites contain a significant amount of proline and glycine, amino acids necessary for collagen synthesis.
- Berries: Rich in vitamin C, which is essential for the formation of stable collagen fibers. Examples include strawberries, raspberries, blueberries and blackberries.
- Citrus Fruits: Another excellent source of vitamin C; oranges, grapefruits and lemons can help support healthy collagen levels.
- Nuts & Seeds: Almonds, walnuts and chia seeds provide essential nutrients like copper that play a role in maintaining optimal collagen production.
Maintaining an adequate intake of these foods or considering supplements if needed will ensure your body has sufficient resources to produce enough collagen for overall health benefits. Remember always to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Collagen is a key element of our bodies, obtainable from numerous origins. By understanding the various sources, we are able to make informed decisions about how best to increase our collagen intake. Now let's look at how the body uses this essential protein for skin health, joint mobility, and bone strength.
How Does the Body Use Collagen?
Collagen is a crucial element for sustaining health and wellness, particularly in terms of skin, joint, and bone health. In this section, we will discuss how the body utilizes collagen to maintain these critical areas.
Role in Skin Health and Appearance
The primary function of collagen in the skin is to provide structure and elasticity. As we age, our bodies produce less collagen naturally, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. By maintaining adequate levels of collagen through diet or supplements, you can help keep your skin looking youthful and healthy.
List of benefits for skin:
- Improves elasticity
- Promotes hydration
- Reduces fine lines and wrinkles
- Increase dermal density
Role in Joint Health and Mobility
Joints are made up of cartilage which contains high amounts of collagen. This protein helps maintain joint flexibility by providing cushioning between bones during movement. When there's a decline in natural production due to aging or other factors such as injury or inflammation,collagen supplementation may be beneficial for improving joint mobility,. Studies have indicated that ingesting hydrolyzed type II collagen can be advantageous in reducing ache related to osteoarthritis and aiding overall joint wellbeing.
List of benefits for joints:
- Promotes flexibility li >
- Maintains cartilage health
- Reduces joint pain and inflammation
- Improves overall mobility li >
Role in Bone Health and Strength
Bones are made up of a matrix that consists primarily of collagen fibers. These fibers provide strength, flexibility, and support to the bone structure. As we age, our bones lose density due to decreased collagen production, leading to an increased risk of fractures or osteoporosis. By maintaining adequate levels of collagen through diet or supplementation,you can help improve your bone health,. Supplementation with certain types of collagen has been shown to raise bone mineral density and lessen the risks related to osteoporosis.
List of benefits for bones:
- Increase bone mineral density
- Promotes flexibility within the bone structure
- Reduces fracture risks
- Maintains overall skeletal integrity
Collagen is a critical component for preserving overall health and wellness, so it's essential to comprehend how the body utilizes it. To ensure that you're getting enough of this beneficial nutrient, let's take a look at recommended daily intake guidelines and factors affecting individual needs.
How Much Collagen Should I Take?
When it comes to collagen intake, the amount you should consume depends on various factors such as your age, health goals, and dietary preferences. In this section, we will discuss the recommended daily intake guidelines for collagen and explore some factors that may affect individual needs.
Recommended Daily Intake Guidelines
The optimal daily dosage of collagen varies depending on the specific type of supplement being used and its intended purpose. A suggested dosage is to take between 10-20 grams of hydrolyzed collagen daily for overall wellbeing. Some studies suggest that taking 5 grams per day can improve skin elasticity and hydration while higher doses (up to 15 grams) may be necessary for joint pain relief or bone health support.
- Skin Health: For improving skin appearance and reducing signs of aging, a dose ranging from 2.5 - 10 grams per day is typically recommended.
- Joints & Mobility: To promote joint health and reduce inflammation or discomfort associated with arthritis or exercise-induced stressors, consider consuming between 8 -12 grams daily.
- Bone Health: Aiming for an intake of around 10-15 grams each day can help maintain strong bones by supporting bone density levels in older adults at risk for osteoporosis.
Factors Affecting Individual Needs
Individual needs for collagen consumption vary based on age, lifestyle habits, dietary choices and existing health conditions. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Age: As we age, our body's natural collagen production declines, making supplementation more important for maintaining optimal levels.
- Lifestyle Habits: Smoking or excessive sun exposure can accelerate the breakdown of collagen in your skin, increasing the need for additional intake through diet or supplements.
- Diet Choices: Vegetarians and vegans may have lower dietary sources of collagen due to their plant-based diets; thus, they might benefit from consuming a higher amount via supplementation using plant-derived options like marine algae-based products.
- Existing Health Conditions: Individuals with certain medical conditions such as osteoarthritis or inflammatory bowel disease may require higher doses of collagen to support joint health and gut function respectively.
In conclusion, it is essential to consider your individual needs when determining how much collagen you should take daily. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen is always recommended for personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances.
It is important to consult a doctor before beginning any collagen supplement regimen, as individual needs may vary. Next, let's consider the duration of effectiveness and changes to skin wellness and joint flexibility that collagen supplements can bring.
How Long Does it Take for Collagen Supplements to Work?
When considering collagen supplements, many people wonder how long it will take before they start noticing the benefits. The duration varies depending on individual factors and the specific effects you are looking to achieve.
Effects on Skin Health and Appearance
The impact of collagen supplements on skin health may become noticeable within a few weeks to a couple of months. A study published in Nutrients found that participants who took 2.5-5 grams of collagen peptides daily experienced significant improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and overall appearance after eight weeks.
- Elasticity: Improved skin elasticity can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Hydration: Properly hydrated skin appears more youthful and radiant due to its ability to retain moisture better than dehydrated skin.
- Density: Increased collagen density contributes to firmer, smoother-looking skin with fewer visible imperfections such as sagging or cellulite.
Effects on Joint Health and Mobility
The time frame for experiencing joint health benefits from taking collagen supplements is typically longer than that for seeing improvements in your complexion. According to a study published in the journal Current Medical Research & Opinion, individuals suffering from osteoarthritis noticed significant reductions in pain after taking 10 grams of hydrolyzed collagen per day for at least three months (source). Another study demonstrated positive results within four months when using undenatured type II collagen (source).
It is important to remember that individual results may vary, and factors such as age, lifestyle habits, and overall health can influence the effectiveness of collagen supplements. For maximal collagen absorption, think about supplementing with vitamins like C or hyaluronic acid.
Supplementing with collagen may offer potential benefits to overall health, however the outcomes of taking it can be unpredictable. Moving on from this topic, let's look at how you can restore collagen in the face through dietary changes, topical treatments and professional treatments.
How to Restore Collagen in the Face
Restoring collagen in the face is necessary for preserving a youthful and healthy look. There are several methods you can use to boost your facial collagen production, ranging from dietary changes to professional treatments. In this section, we will explore various ways of increasing facial collagen levels.
Dietary Changes for Increasing Facial Collagen Production
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support collagen synthesis is crucial for restoring facial collagen. Some key foods and nutrients include:
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and leafy greens, vitamin C plays an essential role in collagen synthesis.
- Protein-rich foods: Consuming protein sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products or plant-based alternatives such as beans and legumes provides amino acids necessary for building new collagen.
- Bone broth: Rich in natural gelatin (which breaks down into collagen), bone broth can be consumed on its own or used as a base for soups and stews.
- Zinc-containing foods:Oysters are an excellent source of zinc which supports skin health by aiding with cell renewal processes.
Topical Treatments for Increasing Facial Collagen Production
In addition to dietary changes, topical treatments can help restore facial collagen levels. These skincare products often contain ingredients known to stimulate the production of new proteins while protecting existing ones from damage caused by environmental factors like UV radiation or pollution.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids are a popular skincare ingredient that can help boost collagen production. Retinoids, such as retinol or tretinoin, can improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of wrinkles when applied topically.
- Vitamin C serums: Applying a topical vitamin C serum can provide antioxidant protection while promoting collagen synthesis in the skin. Look for formulations with L-ascorbic acid, which is considered the most effective form of topical vitamin C.
- Growth factors: Skincare products containing growth factors (naturally occurring proteins) may stimulate collagen production by activating cells responsible for new protein synthesis. These products often come in serum or cream forms.
Professional Treatments for Increasing Facial Collagen Production
If you're looking for more advanced methods to restore facial collagen levels, professional treatments may be an option worth considering. Some popular procedures include:
- Microneedling: This minimally invasive treatment involves creating tiny punctures in the skin using small needles, stimulating natural healing processes and encouraging new collagen formation.
- Laser therapy: Non-ablative laser treatments heat up deeper layers of the skin without damaging its surface layer, triggering increased collagen production as part of the body's response to this controlled injury. li > Chemical peels: By removing dead cells on your face's outermost layer through chemical exfoliation , these peels promote cell turnover rate and encourage new tissue development including fresh collagen fibers . li >
Note that it's essential to consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare professional before undergoing any of these treatments, as they can help determine the most suitable option for your specific skin type and concerns.
A variety of methods exist to boost collagen production in the face, which is a key element for healthy skin. It is important to be mindful that overdoing collagen intake may lead to possible negative effects.
Potential Side Effects of Taking Too Much Collagen
While collagen supplements can provide numerous health benefits, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects that may arise from taking too much collagen. Some individuals might experience gastrointestinal issues, allergic reactions, or interactions with medications.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Taking excessive amounts of collagen supplements could lead to gastrointestinal problems, such as bloating, gas, and stomach cramps. It is essential to observe the prescribed daily dosage and speak with a medical professional if there are any worries regarding one's intake.
Allergic Reactions
Some people might be allergic to specific sources of collagen used in supplements. For instance, those who are allergic to fish should avoid marine-based collagen products. It's essential to read product labels carefully and choose a supplement derived from a source that does not trigger an allergic reaction.
Interactions with Medications
In some cases, taking high doses of collagen supplements could potentially interact with certain medications or medical conditions. Before beginning any supplementation regimen, it is wise to seek medical advice if you are taking medication or have existing health conditions.
To ensure safe consumption and reap the full benefits offered by this vital protein without risking unwanted side effects; adhere closely to recommended dosages for optimal results.
Frequently Asked Questions Collagen
Is there science behind taking collagen?
Yes, numerous scientific studies support the benefits of taking collagen supplements. Research has shown that collagen supplementation can improve skin elasticity, hydration, and reduce wrinkles. Additionally, it may promote joint health and alleviate osteoarthritis symptoms. However, more extensive research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects.
Is there evidence for the benefits of collagen?
Evidence supports various benefits of collagen intake such as improved skin health, increased joint mobility, and enhanced bone strength. Collagen also plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy hair and nails. However, individual results may vary depending on factors like age, lifestyle choices, and existing medical conditions.
What are the side effects of taking collagen?
Potential side effects of consuming excessive amounts of collagen include gastrointestinal issues (bloating or diarrhea), allergic reactions (rashes or difficulty breathing), or interactions with certain medications (blood thinners). It's essential to follow recommended daily intake guidelines and consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
What are 3 facts about collagen?
- Collagen is the most abundant protein in our body; it provides structure to our skin, bones, tendons & ligaments.
- The human body produces less natural collage as we age leading to signs like wrinkles & weaker joints.
- In addition to dietary sources like bone broth & fish skins; supplements derived from bovine or marine sources can help increase one's collagen intake.
Conclusion
In summary, collagen is a key component of our body and its consumption can provide numerous benefits to one's health. Taking the right amount of collagen supplements can help to improve your skin health, joint function, and overall wellbeing. Nevertheless, excessive consumption of collagen may bring about undesirable consequences, so make sure to stick to the prescribed dosage as advised by your medical professional. Remember that eating foods rich in natural sources of collagen such as eggs or fish may also be beneficial for maintaining optimal levels of this essential protein within the body.
Sign up to our newsletter and enjoy 10% off one order
Post related products
-

-

-

Look Younger CIBD0073
















