Can Low Magnesium Cause Hair Loss?
Published:
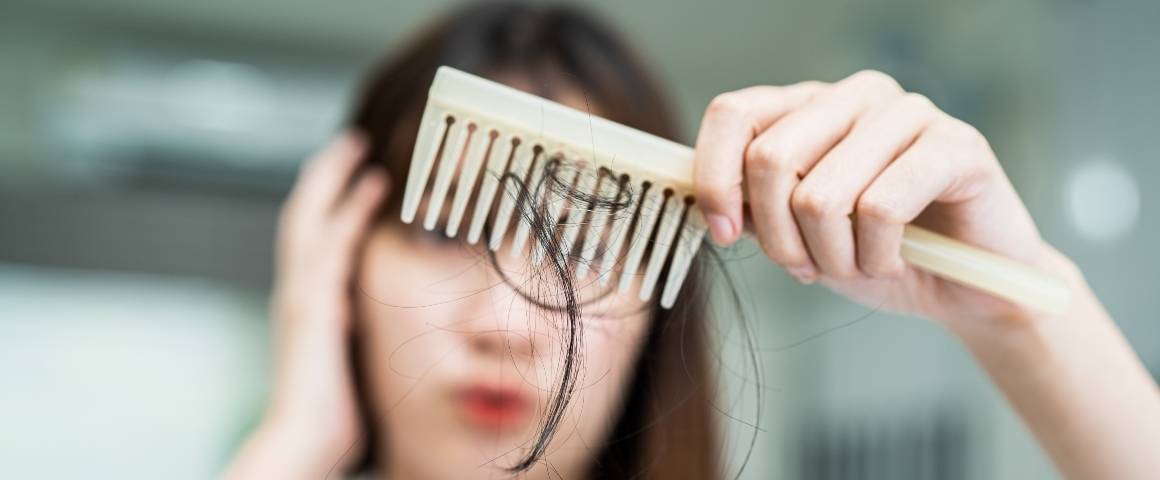
Hair loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormones, medical conditions and nutrient deficiencies. One nutrient that may play a role in hair health is magnesium.
Contents:
- What Is Magnesium?
- Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
- Can Low Magnesium Cause Hair Loss?
- Are Magnesium Supplements Effective for Hair Loss?
- Top Magnesium-Rich Food Sources
- Other Tips to Prevent Hair Loss
- Should I Take a Magnesium Supplement for Hair Loss?
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions on Low Magnesium and Hair Loss
Magnesium is an essential mineral that has many important functions in the body. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control and blood pressure regulation (1).
Some research has found that magnesium deficiency may be linked to hair loss. This article reviews the evidence on the relationship between low magnesium levels and hair loss.

What Is Magnesium?
Magnesium is the fourth most abundant mineral in the human body after calcium, potassium and sodium (2).
It is found in higher concentrations in the bones, muscles and non-muscular soft tissues. Nearly 60% of magnesium in the body resides in the skeletal system (3).
Magnesium plays a variety of roles in the body:
- It activates enzymes needed for energy production, protein formation and nucleic acid synthesis (4).
- It helps regulate blood pressure, blood glucose and nerve transmission (5).
- It aids the contraction and relaxation of muscles (6).
- It helps build teeth and bones (7).
The recommended daily intake (RDI) for magnesium is 400–420 mg per day for men and 310–320 mg per day for women (8).
Magnesium is found naturally in many foods, including dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fish, beans, whole grains, avocados, yogurt, bananas and dark chocolate (9).
It is also available as an oral supplement. Common forms include magnesium oxide, magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate.
Signs and Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
The body tightly regulates magnesium balance, and a severe deficiency is rare. However, many people may be at least mildly deficient (10).
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can include (11, 12):
- Fatigue
- Muscle cramps or twitches
- Insomnia
- Anxiety
- Restless leg syndrome
- Migraines
- Osteoporosis
- High blood pressure
Testing magnesium levels through a blood test provides limited information. Less than 1% of the body's magnesium is found in the blood, and levels are kept in a narrow range (13).
A more accurate approach may be evaluating dietary intake along with symptoms. If low magnesium intake is detected, increasing dietary sources may help resolve deficiency.
Can Low Magnesium Cause Hair Loss?
There are a few pieces of evidence that suggest a link between low magnesium levels and hair loss.
Magnesium Is Vital for Hair Growth
Magnesium is essential for many cellular functions and biological processes. In regards to hair, it plays a role in:
- Protein synthesis: Magnesium is needed to activate an enzyme called ribonucleic acid polymerase that’s crucial for protein formation (14). Hair follicles require adequate protein intake for strong, healthy hair growth (15).
- Energy production: Magnesium aids the body’s generation of energy from food (ATP synthesis) (4). The hair growth cycle is an energy-intensive process that relies on adequate energy supply (16).
- Regulation of hormones: Magnesium may help regulate levels of parathyroid hormone and vitamin D, which are involved in hair follicle cycling (17, 18).
- Regulation of inflammation: Magnesium has anti-inflammatory effects in the body that may promote hair growth, as inflammation can inhibit the hair growth cycle (19, 20).
Therefore, chronic low intakes or deficiency of this mineral could theoretically disrupt these processes and contribute to impaired hair growth.
Observational Studies
A few observational studies have found an association between low magnesium levels and hair loss.
In one study in 30 women with hair loss, 70% had lower serum magnesium levels compared to healthy controls (21).
Another study showed that serum zinc and magnesium levels in women with hair loss were significantly lower than in normal subjects (22).
In a study in 187 people with alopecia areata, an autoimmune disease that causes patchy hair loss, serum magnesium was significantly lower than in those who did not have the condition (23).
While these observational studies suggest a link, they cannot prove that magnesium deficiency itself caused hair loss. More rigorous controlled studies are needed.
Magnesium Improved Hair Growth in Animal Studies
Several animal studies also indicate that magnesium may play a role in hair health.
In one study in mice, a magnesium-deficient diet caused disrupted hair follicle cycling and structure compared to a control diet (24).
Another study showed that treating with magnesium-L-ascorbyl-phosphate (a magnesium compound) improved hair regrowth in mice compared to no treatment (25).
These findings provide some evidence that optimal magnesium levels may benefit hair growth in other mammals. However, human controlled studies are needed to confirm this effect.
Are Magnesium Supplements Effective for Hair Loss?
While there is some evidence linking low magnesium levels to hair loss, there is limited research on whether magnesium supplementation is effective for treating it.
One small, 16-week study in 40 people with hair loss found that taking a daily magnesium and vitamin B6 supplement significantly increased hair numbers compared to placebo treatment (26).
Participants took a magnesium dose of about 200 mg per day, along with 2 mg/day vitamin B6.
However, current evidence is insufficient to determine whether magnesium supplements can reverse hair loss. Larger, longer-term studies are needed to confirm any benefits.
Top Magnesium-Rich Food Sources
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium is 400–420 mg per day for adult men and 310–320 mg per day for adult women (8).
Here are some excellent dietary sources of magnesium (27):
- Pumpkin seeds (156 mg per ounce/28 grams)
- Spinach, boiled (78 mg per cup/180 grams)
- Swiss chard, boiled (75 mg per cup/175 grams)
- Dark chocolate (64 mg per ounce/28 grams)
- Almonds (80 mg per ounce/28 grams)
- Black beans (60 mg per cup/172 grams)
- Avocado (44 mg per cup/150 grams)
- Salmon (26 mg per 3 ounces/85 grams)
- Banana (37 mg per medium fruit)
- Cashews (74 mg per ounce/28 grams)
Including more magnesium-rich whole foods like these in your diet can help maximize intake without supplementation.
Other Tips to Prevent Hair Loss
In addition to optimizing magnesium intake, other strategies can support healthy hair growth. These include:
- Meeting protein needs of around 0.8 grams per kg of body weight per day or more (15).
- Consuming omega-3 fatty acids from fish, walnuts and flaxseed (28).
- Getting enough vitamin D from sunlight, food or supplements (29).
- Managing stress through yoga, meditation and other relaxation techniques (30).
- Treating any scalp conditions or infections that can lead to hair loss.
- Using hair products and styles that avoid damage and breakage (31).
Should I Take a Magnesium Supplement for Hair Loss?
Research on magnesium for hair loss is currently limited. Work with your healthcare provider to determine if a supplement may benefit you.
In some cases, doctors may recommend magnesium supplements for deficiency, such as:
- Poor dietary intake of magnesium-rich foods.
- Digestive disorders like celiac disease that impair nutrient absorption.
- Alcohol dependence.
- Type 2 diabetes.
Until more research is available, focus on meeting the RDA for magnesium intake through whole food sources.
Additionally, take care to get sufficient protein, omega-3s, vitamins and minerals. Managing stress, scalp conditions and hair damage may also promote healthy hair.
Summary
Magnesium is an essential mineral for many bodily processes, including some that may benefit hair growth.
Observational studies show that low magnesium levels are linked to an increased risk of hair loss. However, these studies cannot prove cause and effect.
Initial research in animals and a small human study found that magnesium supplements may improve hair numbers. However, large controlled studies are needed.
For now, there is not enough quality evidence to recommend magnesium supplements for hair loss. Eating a diet rich in magnesium-containing foods remains the best way to prevent deficiency.
Focusing on an overall healthy lifestyle with proper nutrition, stress management and hair care practices may offer the most benefits for maximizing hair health and minimizing loss.
Frequently Asked Questions on Low Magnesium and Hair Loss
What is magnesium and what does it do in the body?
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays many important roles, including protein synthesis, energy production, hormone regulation, and controlling inflammation and blood pressure. It helps activate over 300 enzymes and is vital for many processes.
What are the symptoms of magnesium deficiency?
Mild magnesium deficiency is common. Symptoms can include fatigue, muscle cramps, insomnia, anxiety, restless legs, migraines, and more. Severe deficiency is rare.
What are good dietary sources of magnesium?
Pumpkin seeds, spinach, Swiss chard, dark chocolate, almonds, black beans, avocado, salmon, cashews, and bananas are all excellent sources. Aim for 400mg daily for men, 310mg for women.
Can low magnesium cause hair loss?
There is some evidence that it may contribute to hair loss, but more studies are needed. Magnesium aids protein synthesis, energy production, hormones, and inflammation - all factors in hair growth. Some studies show links between low magnesium and hair loss. Animal studies also show magnesium deficiency disrupts hair growth.
Should I take a magnesium supplement for hair loss?
There is not enough evidence yet to recommend supplements specifically for hair loss. Eating magnesium-rich foods is best to prevent deficiency. Work with your doctor to determine if you need supplementation for other reasons like digestive disorders or diabetes.
What does the research say about magnesium and hair loss?
Small observational studies show associations between low magnesium levels and increased hair loss. One study found magnesium supplements helped increase hair numbers. However, large controlled studies are still needed. The current research shows a possible link, but is too limited to prove cause and effect.
How could magnesium help with hair growth?
Magnesium may promote hair growth by aiding protein synthesis for hair follicles, supporting energy production, regulating hormones and vitamin D, and controlling inflammation. All these factors influence hair follicle health.
Are there risks to taking too much magnesium?
Too much magnesium from supplements can cause diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps, and other gastrointestinal side effects. Very high doses may lead to irregular heartbeat and cardiac arrest. Stick to recommended daily amounts unless advised by your doctor.
Are there other nutrients important for hair health?
Yes, getting enough protein, omega-3s, iron, zinc, vitamin D, vitamin C, and B vitamins may help optimize hair growth and minimize loss. A balanced, nutritious diet supports healthy hair.
What other tips can help with hair loss?
Manage stress, treat scalp conditions, use gentle hair products/styling, get sunlight exposure, prioritize sleep, and manage medical conditions linked to hair loss like thyroid disorders. Your overall health habits significantly influence hair health.
Should I see a doctor for hair loss?
Yes, meet with your doctor, especially if hair loss is severe or getting worse quickly. They can check for underlying conditions and nutrient deficiencies, and discuss treatment options like supplements, medications, laser devices, and procedures.
While magnesium may play a role in hair growth, more research on supplements for hair loss is needed. Focus on getting enough magnesium from foods and maintaining overall health for the best hair health benefits. Work with a healthcare provider for ongoing hair loss.